Region
Abdominal Imaging

Abdominal Wall and Inguinal Region
CT Imaging
This image reveals some of the muscles and structures comprising the abdominal wall. Viewing a cross-section such as this may prove helpful in appreciating the various "layers" of the abdomen. Structures appearing bright are due to the presence of contrast material given both orally and intravenously, thus highlighting the intenstinal lumen and the intravascular space.
Identify the following structures:
- Superficial Fascia
- Rectus Abdominis
- Linea Alba
- External Oblique
- External Oblique Fascia
- Internal Oblique
- Transversus Abdominis
- Transversus Abdominis Fascia And Transversalis Fascia
- Psoas Major
- Quadratus Lumborum

Abdominal Wall Questions
Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Which structure forms the medial border of the rectus sheath?
inguinal ligament
linea alba
semilunar line
tendinous intersection
transumbilical plane
Practical Quiz
Quiz
Upper GI Tract
Upper GI Study
This test involves the oral ingestion of barium, a radio-opaque substance, in order to image the upper digestive tract. It is important to remember that the study highlights intraluminal anatomy (the intestinal wall is not directly visualized, only the interface between barium in the lumen and the intestinal wall)
Identify the following structures:
- Fundus Of The Stomach
- Gastric Folds (Rugae)
- Body Of The Stomach
- Angular Notch (Incisura)
- Antrum Of The Stomach
- Pyloric Sphincter
- Pyloric Canal
- Duodenum

This exam is from a different patient. The barium has moved through the duodenum and into the jejunum. Note that the differentiation of the 3rd from 4th part of the duodenum is not always clearly delineated.
Identify the following structures:
- Fundus Of The Stomach
- Lesser Curvature
- Greater Curvature
- Pylorus
- 1st Part Of Duodenum
- 2nd Part Of Duodenum
- 3rd Part Of Duodenum
- 4th Part Of Duodenum
- Jejunum

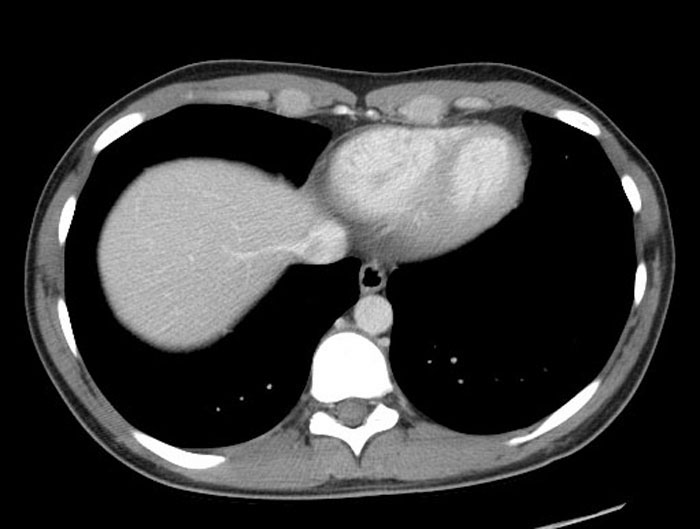
CT: Axial Abdomen
This is an axial image of the upper abdomen from a CT angiogram; the scan was performed when the IV contrast was located within the arteries, before it reached the organs. Notice the pancreas and liver are dark gray, as they have not yet taken up IV contrast. The spleen is brighter, and is just starting to accumulate IV contrast.
Identify the following structures:
- Aorta
- Celiac Trunk
- Splenic Artery
- Common Hepatic Artery
- Pancreas
- Spleen
- Liver
- Diaphragm

Identify the following structures:
- Right Lobe Of The Liver
- Left Lobe Of The Liver
- Falciform Ligament
- Stomach
- Spleen
- Aorta
- Crura Of The Diaphragm
- Splenic Vessels
- Proper Hepatic Artery
- Portal Vein
- Inferior Vena Cava
- Caudate Lobe Of The Liver
- Left Colic (Splenic) Flexure

ERCP
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio-Pancreatography
This is a specific procedure to image the biliary tract. It is done by passing an endoscope orally past the stomach and down into the duodenum where radio-opaque dye is selectively injected into the major duodenal papilla (ampulla of Vater) for fluoroscopic visualization of the biliary tree.
Identify the following structures:
- Endoscope
- Gallbladder
- Cystic Duct
- Common Hepatic Duct
- Right Hepatic Duct
- Left Hepatic Duct
- Common Bile Duct
- Main Pancreatic Duct

MRCP
Magnetic Resonance Cholangio-Pancreatography
This is a specific MRI sequence which is performed to image the biliary tract and pancreatic duct. It is a heavily T2 weighted MRI sequence where any fluid containing structure appears high signal intensity (white) on the image. The background tissues are subtracted out of the images and therefore poorly seen.
Identify the following structures:
- Intrahepatic Bile Ducts
- Common Hepatic Duct
- Cystic Duct
- Common Bile Duct
- Main Pancreatic Duct
- Accessory Pancreatic Duct
- Gallbladder
- Duodenum
- Stomach

Liver Dissection
Upper GI Questions
Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Which part of the duodenum does the common bile duct typically empty into?
1st part (duodenal bulb)
2nd (descending) part
3rd (transverse) part
4th (ascending) part
Lower GI Tract
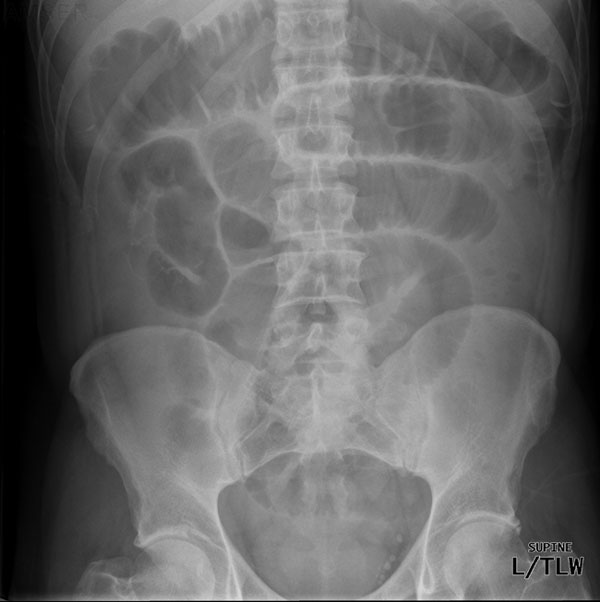
Abdominal Radiograph
This is a supine abdominal radiograph. This patient's small bowel is abnormally dilated, however it demonstrates the fold patterns and differentiating features of the intestines well.
Identify the following structures:
- Transverse Colon
- Jejunum
- Ileum
- Descending Colon
Small Bowel Study
This exam was performed by administering barium and air into the small bowel, to slightly distend and opacify the bowel loops. Note the difference in fold pattern of the jejunum and ileum.
Identify the following structures:
- Jejunum
- Ileum
- Plicae Circulares
- Normal Peristalsis

Barium Enema
This imaging study is similar to the upper GI study. It involves administration of barium rectally, which coats the colon wall, and insufflation of the colon with air to provide a "double contrast" view of the colon.
Identify the following structures:
- Cecum
- Ascending Colon
- Right Colic (Hepatic) Flexure
- Transverse Colon
- Left Colic (Splenic) Flexure
- Descending Colon
- Sigmoid Colon
- Rectum

CT: Axial Lower Abdomen
This is an axial image of the mid-abdomen demonstrating the position of the various segments of the colon. The hepatic flexure contains stool, which often appears bubbly due to the air within it. The transverse and descending colon are both decompressed and therefore appear small in caliber. The small bowel is high density from the ingested oral contrast.
Identify the following structures:
- Liver
- Hepatic Flexure Of Colon
- Transverse Colon
- Descending Colon
- Small Bowel

CT: Coronal Abdomen
These images are reformatted from an oral and IV contrast enhanced abdominal CT scan. The image on the left is the most anterior and that on the right the most posterior. These images demonstrate how the colon serves to "frame" the small bowel, which is located centrally.
Identify the following structures:
- Ascending Colon
- Proximal Transverse Colon
- Transverse Colon
- Distal Transverse Colon
- Descending Colon
- Cecum
- Appendix
- Terminal Ileum

Lower GI Questions
Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Which choice below lists all parts of the bowel that are retroperitoneal?
ascending and descending colon
duodenum, ascending and descending colon
duodenum, jejunum, ascending and descending colon
duodenum, jejunum, ascending, transverse and descending colon
duodenum, jejunum, ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon
Abdominal Angiography
AP View
This is an arteriogram of the abdominal aorta, commonly called an "aortogram". The right femoral artery was cannulated with a catheter, which was advanced into the abdominal aorta to inject contrast.
Identify the following structures:
- Catheter
- Abdominal Aorta
- Renal Arteries
- Common Iliac Arteries
- External Iliac Arteries
- Internal Iliac Arteries
- Lumbar Segmental Arteries
- Inferior Mesenteric Artery
- Median Sacral Artery

Lateral View
This is an arteriogram of the abdominal aorta, commonly called an "aortogram". The right femoral artery was cannulated and the contrast injected via a catheter placed into the abdominal aorta.
Identify the following structures:
- Catheter
- Abdominal Aorta
- Celiac Trunk
- Superior Mesenteric Artery
- Vertebral Column

Celiac Trunk (axis) angiogram
This is a selective angiogram of the celiac trunk. Contrast has been injected through the tip of the catheter which is in the celiac trunk. Note that the bony anatomy is visible, it has not been 'subtracted' from view. Note that the celiac trunk is at the L1 vertebral body level.

Renal CT Angiogram
This thick axial image is part of a CT angiogram, where contrast dye is injected into a peripheral vein for optimal imaging of the vasculature. This image was taken when the contrast material was in greatest concentration in the arterial system, making the arteries bright.
Identify the following structures:
- Abdominal Aorta
- Renal Arteries
- Renal Veins
- Inferior Vena Cava
- Renal Cortex
- Renal Medulla
- Renal Collecting System
- Renal Sinus
- Superior Mesenteric Artery

Superior Mesenteric Angiogram
This is a selective angiogram of the superior mesenteric artery. Note that the tip of the catheter is in the proximal SMA. Some of the injected contrast refluxes back into the aorta. Note that the bony anatomy has been 'subtracted' from view by a computer program in order to focus on the vascular anatomy.
Identify the following structures:
- Catheter
- Superior Mesenteric Artery
- Jejunal Branches
- Ileal Branches
- Ileocolic Artery
- Right Colic Artery
- Middle Colic Artery

This is the same image unsubtracted (i.e. with bones).

Portal Venogram
This angiogram of the portal vein was obtained during a special procedure known as a TIPS procedure (transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt) which is performed for relief of portal hypertension. A catheter (white line descending from the middle portion of the top of the image) has been placed from the right internal jugular vein, through the superior vena cava, through the right atrium and out the right hepatic vein. The catheter then travels through the liver parenchyma and into the right branch of the portal vein. The tip of the catheter is in the splenic vein. Contrast was injected through this catheter to obtain this image.
Identify the following structures:
- Catheter
- Splenic Vein
- Superior Mesenteric Vein
- Portal Vein
- Right And Left Branches Of Portal Vein
- Left Gastric Vein

Inferior Mesenteric Angiogram
This is a selective angiogram of the inferior mesenteric artery. The contrast is filling the inferior mesenteric artery and its branches. Note that the bony anatomy has been 'subtracted' from view by a computer program in order to focus on the vascular anatomy.
Identify the following structures:
- Inferior Mesenteric Artery
- Left Colic Artery
- Sigmoidal Arteries
- Superior Rectal Artery

This is same image unsubtracted (i.e. with bones).Note that in the unsubtracted image, the contrast that has been excreted into the renal collecting systems is visible.

Lateral CTA: Abdominal Aorta
This is a lateral reconstruction of a CTA showing the celiac trunk and SMA.
Identify the following structures:
- Abdominal Aorta
- Celiac Artery
- Superior Mesenteric Artery

Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Axial Slices
Identify the following structures:
- Inferior Vena Cava
- Liver
- Right Hepatic Vein
- Descending Aorta
- Esophagus
- Azygous Vein
- Hemiazygous Vein
- Right Ventricle
- Left Ventricle