Region
Head & Neck

Skull & Cranial Cavity
Identify the following structures:
- Anterior Arch Of C1
- Posterior Arch Of C1
- Body Of C2
- Dens
- Mastoid Air Cells
- Dorsum Sellae
- Pituitary Fossa
- Floor Of Anterior Cranial Fossa
- Coronal Suture
- Inner Table Of Calvarium
- Outer Table Of Calvarium

Dissection Videos
Osteology and Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Neck
Lateral Cervical Spine
Identify the following structures:
- Anterior Arch Of C1
- Posterior Arch Of C1
- Dens
- Body Of C2
- Occipital Condyle
- Spinous Process Of C2
- Lateral Mass Of C4
- Inferior Facet Of C4
- Superior Facet Of C7
- Pedicle Of C7
- Facet Joint
- Intervertebral Disc
- Intervertebral Foramen

Flexion and Extension of the Cervical Spine
These views are obtained with the patient performing maximal flexion and extension of their neck. They are used to assess alignment of the spine, and to look for ligamentous instability (ligament tears or laxity may result in vertebral bodies slipping forward or backward on each other).


Note that the vertebral bodies remain aligned normally with movement, as is shown by the smooth, continuous posterior spinal line (green dashed line). Note the uniform widening of the interspinous spaces with flexion.


AP Cervical Spine: Vertebral Bodies
Note the numbering of the vertebral bodies.

Odontoid View
This image is taken in an AP projection with the patient's mouth open.
Identify the following structures:
- Odontoid Process (Dens)
- Transverse Process C1
- Lateral Masses Of C1
- Spinous Process Of C2
- Overlapping Occipital Bone

CT Cervical Spine
This images show the cervical spine from the C1/C2 level to the intervertebral disc.
Identify the following structures:
- Odontoid Process (Dens)
- Anterior Arch C1
- Posterior Arch C1
- Lateral Mass C1
- Foramen Transversarium
- Transverse Process C1

CT: Cervical Spine Sagittal & Coronal
These images are reformatted from a helical CT scan of the cervical spine. They are supplementary to axial images and are useful for evaluating alignment and joint spaces. Some fractures, such as compression fractures, are easier to identify on these images, as the loss of height is easier to appreciate.
Identify the following structures:
- Anterior Arch Of C1
- Posterior Arch Of C1
- Dens
- Body Of C2
- Spinous Process C4
- Intervertebral Disc

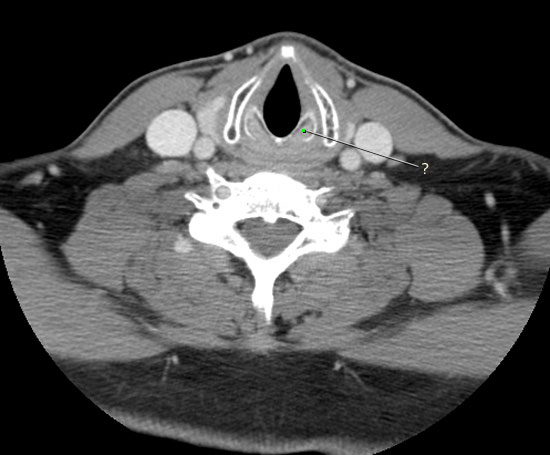
Axial CT
The following images are selected axial CTs of the neck; image 1 is the most superior, and image 6 the most inferior. These were obtained with contrast enhancement. Intravenous contrast helps to distinguish blood vessels from adjacent muscles and lymph nodes, by making them higher attenuation.
Identify the following structures:
- Submandibular Gland
- Epiglottis
- Vallecula
- Left Sternocleidomastoid
- Platysma
- Prevertebral Muscles
- Right Internal Carotid Artery
- Right Internal Jugular Vein
- Right External Carotid Artery
- Left External Jugular Vein

Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Osteology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Afferent neurons from the carotid body and sinus travel in:
accessory nerve
ansa cervicalis
glossopharyngeal nerve
hypoglossal nerve
trigeminal nerve
Face & Scalp
Quiz
The skin of the chin is innervated by:
buccal nerve
infraorbital nerve
marginal mandibular nerve
mental nerve
supratrochlear nerve
Eye & Orbit
Imaging the eye and orbit

Both CT and MRI are used to evaluate the contents of the orbit. When there is a history of trauma, CT is typically used since it is more sensitive for fractures of the bony margins of the orbits. On CT, when viewing soft tissue windows, the extraocular mucles, optic nerve and globe are visible, so limited assessment of these structures can also be made.
The higher soft tissue contrast of MRI results in better conspicuity of the soft tissue structures of the orbit, especially the globe. Compare the MRI and CT images shown.
MRI: Axial T1
The following are T1-weighted axial MRI images of the orbit (thin 2mm sections). The first image is the most inferior. Supsequent images are sequentially more superior. On T1 images, fat is high signal intensity (bright), fluid is low signal intensity (dark), and muscles and nerves are gray.
Identify the following structures:
- Inferior Rectus
- Eyeball (Globe)
- Orbital Fat
- Ethmoid Air Cells

MRI: Axial T2
On T2-weighted images, the high signal intensity fluid of the anterior and posterior chambers contrasts with the dark signal of the lens, making it very conspicuous. The air in the paranasal sinuses and air cells is dark.
Identify the following structures:
- Medial Rectus
- Lateral Rectus
- Optic Nerve
- Anterior Chamber
- Vitreous Chamber
- Lens
- Orbital Fat
- Sphenoid Sinus
- Ethmoid Air Cells

MRI: Coronal T1
This T1-weighted MRI is in the coronal plane just posterior to the globe (eyeball). The extraocular muscles, optic nerves, and superior opthalmic vein can be seen well in this image. Fat is bright, and muscles and nerves are gray.
Identify the following structures:
- Left Optic Nerve
- Medial Rectus
- Inferior Rectus
- Lateral Rectus
- Superior Rectus
- Levator Palpebrae Superioris
- Superior Oblique
- Ethmoid Air Cells
- Maxillary Sinus
- Orbital Fat

CT: Coronal orbit
This is an IV contrast enhanced CT. The blood vessels are opacified with the iv contrast material, which makes them high attenuation. The orbital fat is dark gray, in contrast to the medium gray density of the extraocular muscles.
Identify the following structures:
- Optic Nerve
- Medial Rectus
- Inferior Rectus
- Lateral Rectus
- Superior Rectus & Levator Palpebrae Superioris
- Superior Oblique
- Ophthalmic Artery
- Orbital Fat

CT: Axial orbit
This CT is displayed in soft tissue window.
Identify the following structures:
- Anterior Chamber
- Lens
- Vitreous Chamber
- Medial Rectus
- Lateral Rectus
- Optic Nerve
- Orbital Fat
- Ethmoid Air Cells
- Anterior Clinoid Process

Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Osteology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Which of the following structures does not travel through the common tendinous ring?
abducens nerve
nasociliary nerve
oculomotor nerve
optic nerve
trochlear nerve
Ear
CT: Axial
This is a series of axial images of the head taken at the level of the petrous portion of the temporal bone and inner ear. The series moves from superior to inferior. The images are "windowed" to highlight osseous structures. Each axial image is only 1mm thick! This allows the fine structures of the inner ear to be displayed in detail.

CT: Coronal Ear

This is a coronal CT image taken at the level of the petrous portion of the temporal bone and inner ear. The tympanic membrane is a very thin structure but can be faintly seen on this 1mm thick section.
Quiz
Quiz
Which of the following structures is correctly matched with its location in the middle ear cavity?
entrance to mastoid antrum – inferior wall (floor)
eustachian tube – anterior wall
jugular fossa – posterior wall
pyramidal eminence – medial wall
round window – lateral wall
Deep Face
CT: Axial
This is an axial CT of the face at the level of the lateral pterygoid muscle.
Identify the following structures:
- Condylar Process Of Mandible
- Lateral Pterygoid
- Lateral Pterygoid Plate
- Medial Pterygoid Plate
- Coronoid Process Of Mandible
- Temporalis
- Maxillary Sinus

Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Osteology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Which nerve travels through foramen ovale to enter the deep part of the face (infratemporal fossa)?
facial nerve
inferior alveolar nerve
lingual nerve
mandibular nerve
maxillary nerve
Nasal Cavity
AP Sinuses
On AP view of the sinuses, the petrous ridge of the temporal bone and mastoid air cells overlap and partially obscure the lower orbits and maxillary sinuses. In order to better evaluate the maxillary sinuses, a special view (Waters) is obtained, shown in the next image.
Identify the following structures:
- Inferior Concha (Turbinate)
- Nasal Septum
- Nasal Cavity
- Maxillary Sinus
- Ethmoid Sinus (Air Cells)
- Frontal Sinus
- Petrous Ridge Of Temporal Bone
- Orbit

Waters view of the sinus
A waters view is an AP view in which the patient flexes the neck and elevates the chin so that the x-ray beam passes obliquely through the facial structures, directed from caudal to cranial. In effect, this places the orbits and maxillary sinuses above the skull base structures and petrous ridge of the temporal bone, enabling them to be visualized better than on an AP view. This patient's frontal sinuses are very small (hypoplastic).
Identify the following structures:
- Maxillary Sinus
- Petrous Ridge Of Temporal Bone
- Orbit

Lateral sinuses
Although all of the right and left sided structures are superimposed on the lateral view, it is the best projection to show the sphenoid sinuses, which are obscured by other bony structures on the AP and Waters views. This patient has hypoplastic (underdeveloped) frontal sinuses.
Identify the following structures:
- Sphenoid Sinuses
- Maxillary Sinuses
- Nasal Bones
- Hard Palate
- Nasopharynx
- Metallic Dental Fillings

CT: Coronal nasal cavity

The following images are four sequential coronal sections through the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. The first image is the most anterior and subsequent images are more posterior. Remember, when looking at coronal images, the patient's right side is depicted on the left side of the image.
Identify the following structures:
- Nasal Septum
- Frontal Sinus
- Maxillary Sinus
- Inferior Concha (Turbinate)
- Middle Concha (Turbinate)
- Nasolacrimal Duct

CT: Sagittal midline
This is a 10mm thick reformatted CT image of the nasal cavity showing midline structures.
Identify the following structures:
- Frontal Sinus
- Sphenoid Sinus
- Pituitary Fossa
- Perpendicular Plate Of Ethmoid
- Cribriform Plate (Of Ethmoid Bone)
- Crisa Galli
- Vomer
- Nasal Bone
- Cartilaginous Nasal Septum
- Hard Palate
- Nasopharynx

CT: Axial head (pterygopalatine fossa)
This CT scan has been "windowed" (contrast adjusted) to highlight the bony structures. The pterygopalatine fossa (between the maxillary bone anteriorly and the root of the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone posteriorly) can be appreciated.
Identify the following structures:
- Zygomatic Arch
- Maxillary Sinus
- Pterygopalatine Fossa
- Condyle Of Mandible
- Foramen Ovale
- Foramen Spinosum
- Carotid Canal

Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Practice Questions
Quiz
Which of the following drains into the inferior meatus?
frontal sinus
maxillary sinus
middle ethmoid air cells
nasolacrimal duct
sphenoid sinus
Oral Cavity & Pharynx
The air filled pharynx and trachea are lucent on this lateral view of the soft tissues of the neck.
Identify the following structures:
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx
- Larynx
- Epiglottis
- Soft Palate
- Uvula

CT: Sagittal Neck
This sagittal CT scan has been reformatted from a conventional helical (axial) CT of the neck. It is a midline sagittal view.
Identify the following structures:
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx
- Hard Palate
- Soft Palate
- Uvula
- Oral Cavity
- Epiglottis

CT: Nasopharynx
The following images are axial, contrast enhanced CTs of the neck at the level of the nasopharynx. The first image is superior and the second more inferior.
Identify the following structures:
- Nasopharynx
- Pharyngeal Recess
- Pharyngotympanic (Eustachian) Tube
- Torus Tubarius
- Choana

CT: Oropharynx
The following images are axial, contrast enhanced CTs of the neck at the level of the oropharynx. The first image is superior and the second more inferior.
Identify the following structures:
- Oropharynx
- Submandibular Gland
- Sublingual Gland
- Geniohyoid
- Mylohyoid
- Pharyngeal Constrictors

CT: Laryngopharynx
The following images are axial, contrast enhanced CTs of the neck taken just below the mandible, at the level of the laryngopharyx. The first image is superior and the second more inferior.
Identify the following structures:
- Largyngopharynx
- Epiglottis
- Vallecula
- Pharyngeal Constrictors
- Hyoid Bone

Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Practice Questions: Oral Cavity
Quiz
Which of the following is found between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches?
choanae
palatine tonsil
pharyngeal recess
pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids)
torus tubarius
Anatomy Practice Questions: Pharynx
Quiz
The middle constrictor muscle arises from the:
cricoid cartilage
hamulus
hyoid bone
pterygomandibular raphe
thyroid cartilage
Larynx
CT: Sagittal Neck
This sagittal CT scan has been reformatted from a conventional helical (axial) CT of the neck. It is approximately a midline sagittal view.
Identify the following structures:
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx
- Epiglottis
- Hyoid Bone
- Laryngeal Vestibule
- Thyroid Cartilage
- Larynx

CT: Upper Larynx
This contrast enhanced CT scan of the neck is at the level of the piriform fossa & aryepiglottic folds. The laryngopharyx is relatively flattened, not distended with air.
Identify the following structures:
- Aryepiglottic Fold
- Piriform Fossa
- Larynx
- Thyroid Cartilage

CT: Mid Larynx
The following images from a contrast enhanced neck CT are from the mid-larynx, just below the glottis. The first image is superior and the second is more inferior. The arytenoid and corniculate cartilages are tough to differentiate from one another on a single axial image.
Identify the following structures:
- Larynx
- Arytenoid/corniculate Cartilage
- Thyroid Cartilage

Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Practice Quiz
Quiz
During a thyroidectomy, the surgeon accidentally cuts the right recurrent laryngeal nerve in the tracheo-esophageal groove. Which of the following describes the expected result?
the accident has not affected the patient’s vocal cord function
the patient’s right vocal cord is completely paralyzed, and sensation is intact
the patient’s right vocal cord is completely paralyzed, and there is no sensation inferior to the glottis on the right side
the patient’s right vocal cord is partially paralyzed, and sensation is intact
the patient’s right vocal cord is partially paralyzed, and there is no sensation inferior to the glottis on the right side
Vasculature
Aortic Arch and Neck CT Angiogram
This is a 3D reformatted image from a CTA (computed tomography angiography) of the aortic arch and neck. CT angiography is performed by scanning the patient while the injected IV contrast (dye) is in the arterial circulation. Helical images are obtained, which can subsequently be reformatted in any plane or in three-dimensions. This image is a three-dimensional volume rendered image.
Identify the following structures:
- Aortic Arch
- Subclavian Arteries
- Common Carotid Arteries
- External Carotid Arteries
- Internal Carotid Arteries

Carotid CT Angiogram
This image from a CT angiogram of the neck has been reformatted in an oblique sagittal plane to evaluate the carotid bifurcation. Several of the external carotid branches can be identified. The hyoid bone and calcified thyroid cartilage are labelled to serve as reference points.
Identify the following structures:
- Common Carotid Artery
- Internal Carotid Artery
- External Carotid Artery
- Lingual Artery
- Facial Artery
- Maxillary Artery
- Vertebral Artery
- Hyoid Bone
- Thyroid Cartilage

MR Angiography - Neck
This MRA (magnetic resonance angiogram) shows the aortic arch, its branches, and arteries of the neck. This image was obtained using IV gadolinium as a contrast agent, with a specialized technique allowing the backround tissues to be suppressed.
Identify the following structures:
- Brachiocephalic Trunk
- Right Subclavian Artery
- Right External Carotid Artery
- Right Internal Carotid Artery
- Left Common Carotid Artery
- Left Internal Carotid Artery
- Left Vertebral Artery
- Left Subclavian Artery

MRI: Cavernous Sinus
In these axial and coronal MRIs, the cavernous sinus can be seen with a few of its important anatomic relationships. Notice the carotid arteries flowing within the cavernous sinuses.
Identify the following structures:
- Left Cavernous Sinus
- Right Cavernous Sinus
- Pituitary

CT Axial Slices
Find below axial slices of the head and neck.
Identify the following structures:
- Globe
- Orbital Fat
- Lacrimal Gland
- Superior Ophthalmic Vein
- Frontal Sinus
- Crista Galli
- Temporalis