Region
Thorax Radiology

Breast
Mammogram (right mediolateral oblique)
This image represents one of the common mammographic views. The breast tissue is compressed in a medial lateral oblique (MLO) orientation in order to obtain a large surface area for imaging. Fibroglandular tissue, the breast ducts and lobules, comprises the bulk of the dense material seen in a mammogram. All normal breast tissue lies superficial to the pectoralis major muscle, and is separated from this muscle by clavipectoral fascia.
Identify the following structures:
- Nipple
- Fibroglandular Tissue
- Pectoralis Major Muscle
- Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue

Ductogram
A ductogram is a procedure performed to visualize the ductal anatomy of a breast lobe, often to evaluate patients with nipple discharge. A very thin, blunt cannula is inserted into the opening of a particular lactiferous duct, and contrast dye is injected followed by mammographic imaging. This example shows the ductal anatomy of a breast lobe, with reflux of dye into the lobular tubuloalveolar system.
Identify the following structures:
- Lactiferous Duct
- Terminal Ducts
- Tubuloalveolar Gland Lobule

Chest Wall
Radiography of the Chest Wall
A chest X-ray (CXR) is one of the most common imaging tests you will encounter as a clinician. Two views (PA and lateral) are obtained at 90 degrees from each other in order to gain an appreciation of dimensionality.
Structures of the chest wall can be evaluated on radiographs. The breast tissue cannot be evaluated on standard CXR due to poor visualization of the breast parenchyma.
In the lateral view, the anterior and posterior limits of the thoracic cavity are visible.

PA Chest - Chest Wall
This is a normal PA chest xray. When the image is taken, the scapula is protracted to minimize its overlap with the chest wall. Can you see where the medial border of the scapula is overlapping with the chest wall? Notice that the anterior and posterior parts of the ribs are superimposed. The portion of the rib that is more horizontal is the posterior part, while the anterior part of the rib slopes from superior to inferior.
Identify the following structures:
- Clavicle
- Scapula
- Ribs

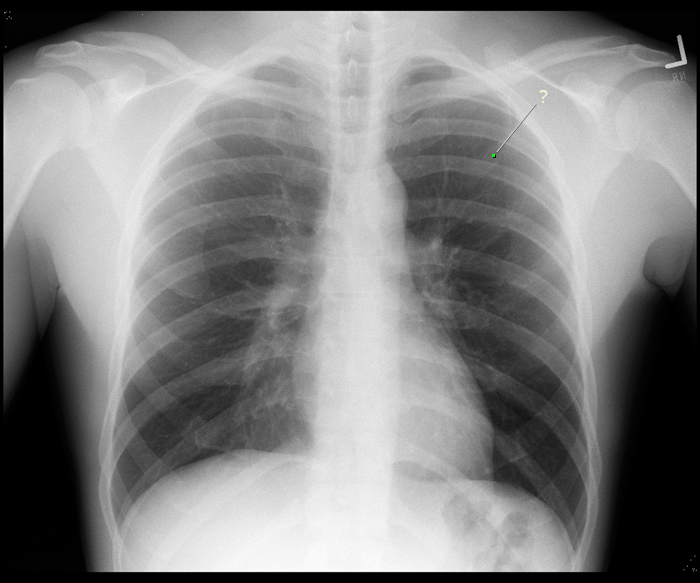
BONUS: Counting ribs on a CXR is a skill that requires some practice. Radiologists typically find rib 1 and count from there. On the right side of the patient, see if you can find the intersection between the anterior part of the 5th rib and the posterior part of the 8th rib. When you add the labels to the image a dot will appear at this intersection.
Chest Wall - Quiz
Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Which part of the rib is labeled?
anterior
posterior
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Which costal cartilage joins the sternum at the sternal angle?
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
Osteology Quiz
Quiz
Practical Quiz
Quiz
Lungs
PA Chest - Lung
Air does not absorb X-ray beams, so areas filled with air, such as the lungs and bronchial tree, appear dark on a CXR. Notice that there are white "streaks" in the lungs, especially near the hilum. These streaks are formed by the branches of the bronchial tree and pulmonary vessels. Notice that in a normal chest film, the right hemidiaphragm is slightly higher than the left hemidiaphragm.
Identify the following structures:
- Trachea
- Right Lung
- Left Lung
- Right Hemidiaphragm
- Left Hemidiaphragm

Lateral Chest - Lung
A lateral film is taken with the left side of the patient against the detector plate to reduce magnification of the heart (structures farther from the detector become magnified). Because of this, the right ribs are slightly magnified and appear larger than the left ribs. Notice that the right and left lungs are superimposed on a lateral film.
Identify the following structures:
- Left Lung
- Right Lung

Lobar Anatomy - PA
Portions of each lobe of the lung are superimposed on one another on a CXR. Because of this, it is not always possible to pinpoint the lobar location of a nodule on a PA CXR.
Identify the following structures:
- Left Upper Lobe
- Left Lower Lobe
- Right Middle Lobe

Lobar Anatomy - Lateral
The lower lobes of each lung are completely superimposed on one another on a lateral CXR, and portions of the upper and right middle lobes are superimposed. Because of this, it is not possible to determine which lung an abnormality is in on a lateral CXR.
Identify the following structures:
- Left Upper Lobe
- Left Lower Lobe

Abnormal Chest Radiograph
Quiz
Lung Dissection Video
Lungs - Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
The horizontal fissure separates:
left upper lobe from left middle lobe
left middle lobe from left lower lobe
left upper lobe from left lower lobe
right upper lobe from right middle lobe
right middle lobe from right lower lobe
right upper lobe from right lower lobe
Practical Quiz
Quiz
Mediastinum
PA Chest Radiograph
Many of the mediastinal structures are of similar density, so it is difficult to differentiate them with radiography. However, structures that are adjacent to the radiolucent lungs (less dense) can be visualized due to the difference in density.
Identify the following structures:
- Heart
- Aortic Knob
- Superior Vena Cava
- Descending Aorta
- Trachea
- Trachial Bifurcation

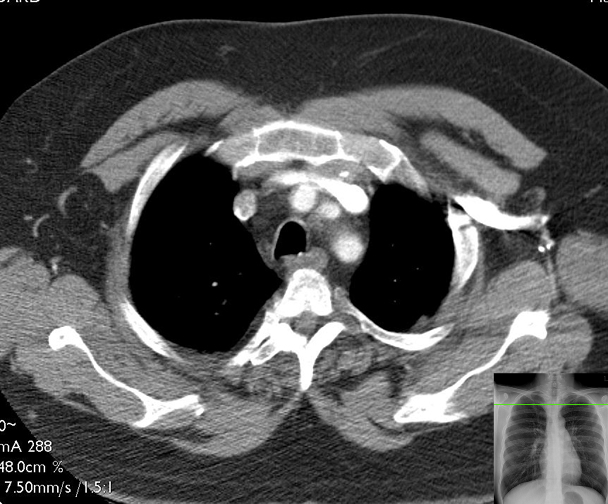
CT: Axial Superior Mediastinum
This is a series of axial (transverse) CT images of the thorax of one patient. The images have been "windowed" (contrast adjusted) in order to highlight soft-tissue structures, and consequently, the lungs appear mostly black. As you work through these images, it may be helpful to remember the structures in the previous "slice" in order to be able to trace those structures and maintain orientation. This first image will ask you to name several structures for reference, most of which will continue to be present in subsequent slices. In all of these images, vascular structures are bright due to the injection of contrast dye in the venous system (usually via the arm) of the patient. You can assume that black represents air. The reference chest radiographs show the approximate level of the axial slice.
Slices
Each of the following CT slices is more caudal than the slice prior.
Identify the following structures:
- Manubrium
- Vertebral Body
- Spinal Cord
- Spinous Process
- Ribs
- Pectoralis Major
- Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
- Scapulae
- Trachea
- Esophagus
- Left Brachiocephalic Vein
- Right Brachiocephalic Vein
- Brachiocephalic (Innominate) Artery
- Left Common Carotid Artery
- Left Subclavian Artery
Mediastinum - Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Your patient has a tumor on the root of the lung - specifically it is located on the posterior aspect of the right primary bronchus. Which of the following would most likely be compressed by the tumor?
Phrenic nerve
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
Sympathetic chain
Thoracic duct
Vagus nerve
Practical Quiz
Quiz
Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Heart
PA Chest Radiograph
The size of the heart and the borders of certain chambers can be evaluated on a PA chest film. By performing the film PA, the heart is placed close to the detector plate, preventing magnification of the heart.
Identify the following structures:
- Right Heart Border
- Left Heart Border
- Aortic Arch
- Superior Vena Cava
- Right Atrium
- Left Ventricle
- Apex

Cardiomegaly
This is a comparison of a normal-sized heart (right image) with an enlarged heart (left image). Notice that the enlarged heart is more globular in shape. The left heart borders is closer to the left lateral chest wall, and the right heart border extends out farther from the spine compared to the normal heart.

Lateral Chest Radiograph
In this view, the anterior and posterior heart borders are visible. There is some superimposition of the heart chambers on this view. The most posterior chamber is the left atrium, and the most anterior chamber is the right ventricle.
Identify the following structures:
- Right Ventricle Border
- Left Atrium Border
- Aortic Arch

CT Heart
This is an axial CT image of the heart. Below are a reference PA chest radiograph and a comparable anatomic image from the Visible man showing the approximate level of this axial slice. As in all axial (transverse) images, the patient is lying supine and you are observing from the patient's feet looking towards the head.
An iodine based CT contrast agent was injected intravenously to opacify (increase the density of) the heart chambers and blood vessels.
Identify the following structures:
- Sternum
- Left Ribs
- Right Pulmonary Vein
- Left Atrium
- Left Ventricle
- Mitral Valve
- Right Atrium
- Right Ventricle
- Interventricular Septum
- Descending Aorta



Coronal CT
This image is of the same patient as in the previous image. CT images are obtained as a helix of data that can then be reformatted into imaging planes. This is a coronal reformated image of the contrast enhanced chest CT.
Identify the following structures:
- Left Venticle
- Myocardium
- Ascending Aorta
- Aortic Valve
- Pulmonary Trunk
- Right Atrium
- Superior Vena Cava
- Interventricular Septum
- Right Ventricle
- Diaphragm

Cardiac Chambers
The borders of each cardiac chamber are not discernable on radiography (except where they are border forming with the lung, like the lateral margin of the right atrium). This demonstrates the approximate position of the chambers and large vessels.
Identify the following structures:
- Right Ventricle
- Left Ventricle
- Right Atrium
- Pulmonary Arteries
- Superior Vena Cava
- Ascending Aorta

Cardiac Chambers on Radiography (Lateral)
This demonstrates the approximate position of the chambers and large vessels on the lateral radiograph.
Identify the following structures:
- Right Ventricle
- Left Ventricle
- Left Atrium
- Main Pulmonary Artery

Imaging the Heart Video
Linked below is a 10 minute introduction into imaging the heart recorded by Nancy McNulty, MD (Professor of Radioloy and Medical Education) that is intented to supplement the material covered in class.
Angiography
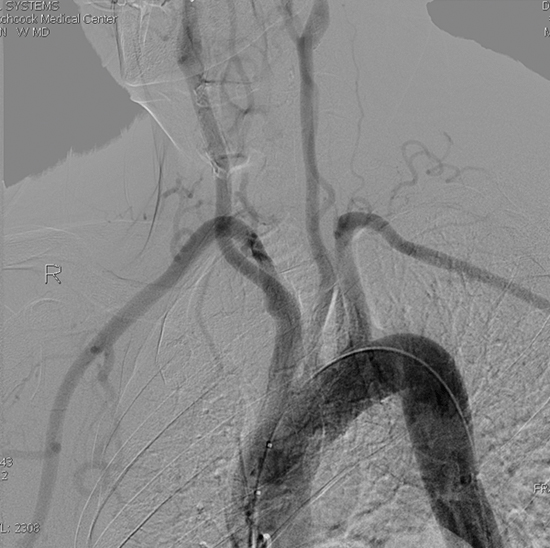
Aortic Arch Angiogram
An aortic arch angiogram is obtained by threading a catheter into the ascending aorta and injecting iodine-based dye. Sequential X-rays are then taken as the dye is injected. This image is a static image from the angiogram series.
Identify the following structures:
- Ascending Aorta
- Brachiocephalic Artery
- Left Common Carotid Artery
- Left Subclavian Artery
- Left Vertebral Artery
- Right Common Carotid Artery
- Right Subclavian Artery
- Right Internal Thoracic Artery
Left Coronoary Angiogram

An angiogram of the coronary arteries is performed by threading a small catheter from the femoral artery in the groin up into the aorta, and selectively cannulating the coronary ostia. Radio-opaque dye is then injected and X-ray images are obtained via fluoroscopy to evaluate the coronary anatomy. Fluoroscopy allows for real-time acquisition of images, and is a technique which is conceptually similar to the standard X-ray radiographs which you have seen thus far. A major difference is that radio-dense material appears dark rather than bright. This image of the left coronary system is obtained via a right anterior oblique view of the heart.
Identify the following structures:
- Anterior Interventricular Artery (Lad)
- Anterior Interventricular Artery (Lad)
- Left Coronary Artery (Left Main Artery)
- Circumflex Artery
- Obtuse Marginal Branch Of The Circumflex Artery
- Atrioventricular Groove Branch Of The Circumflex Artery

Right Coronary Angiogram
This image was obtained via a left anterior oblique view (almost as thought you were looking "down the barrel" of the heart) in order to view the right coronary artery as it courses along the outside of the atrioventricular groove on the right. Because of the angle, the posterior interventricular artery branch will look significantly foreshortened.
Identify the following structures:
- Angiogram Catheter
- Right Coronary Artery
- Branch To Sinoatrial Node
- Posterior Interventricular Artery

Left Ventriculogram
This image is obtained by threading the catheter into the left ventricle and injecting contrast dye. The dynamic ejection of blood into the aorta can then be evaluated.
Identify the following structures:
- Angiogram Catheter
- Left Ventricle (Filling With Contrast Dye)
- Aorta
- Aortic Valve

Heart - Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Which structure is associated with the right ventricle?
Coronary sinus
Fossa ovalis
Mitral valve
Moderator band (septomarginal trabecula)
Pectinate muscles
Practical Quiz
Quiz
Identify the labeled structure.

Superior vena cava
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Aorta
Right coronary artery
Thorax Radiology Quiz
Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Identify the labeled chamber of the heart.

Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left atrium
Left ventricle
Axial CT Slices
Identify the following structures:
- Trachea
- Esophagus
- Right Common Carotid Artery
- Left Common Carotid Artery
- Left Vertebral Artery
- Right Vertebral Artery
- Left Vertebral Vein
- Right Vertebral Vein
- Left Internal Jugular Vein
- Right Lobe Of Thyroid Gland
- Left Lobe Of Thyroid Gland
- Anterior Scalene
- Sternocleidomastoid







