System
Kidney & Retroperitoneum
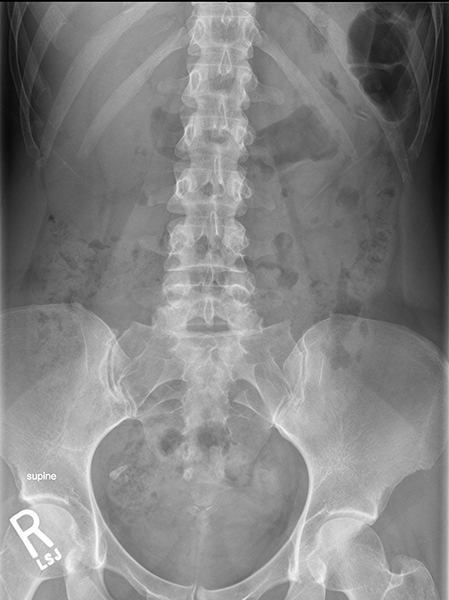
Abdominal Radiograph
Formerly known as a "KUB" (kidneys, ureters, bladder). The abdominal radiograph is indicated for a variety of symptoms and diagnoses. As you have seen in prior radiographs, the tissue boundaries will be identified by differences in the density of adjacent tissue. In the abdomen, often it is the adipose tissue that surrounds an organ which helps to define its boundaries.
KUB Abdominal Radiograph
Identify the following structures:
- Left Kidney
- Right Kidney
- Left Psoas
- Right Psoas
- Bladder
- Stool
Intravenous Pyelogram
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is a specialized radiographic examination of the kidneys, collecting system, and bladder. Contrast dye is injected into an intravenous line, and serial radiographs are obtained as the dye gets filtered and excreted by the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. The anatomy of the renal collecting system, ureters, and bladder, as well as subtle physiologic changes in relative kidney function, can then be assessed.
Identify the following structures:
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Bladder
- Minor Calyx
- Major Calyx
- Renal Pelvis

Kidney Stone
This is a radiograph of a patient with right flank pain. It shows several radiodense right renal stones. After you have reviewed this image and identified the structures, click here to see a CT scan of the same patient in order to see the specific location of the stone.
Identify the following structures:
- Left Kidney
- Right Kidney
- Stones In Right Kidney
- Calcified Costochondral Cartilages

Gallstone
This is a scout image from a CT scan which shows a gallstone. Although the stone is in the right upper quadrant and could be mistaken for a kidney stone, the close association with the liver helps to identify it as a gallstone.
Identify the following structures:
- Liver
- Gallstone

CT Imaging
Axial Abdomen
This is an axial CT image at the level of the kidneys. Oral and intravenous contrast had been administered prior to obtaining the image. Identify normal structures.
Identify the following structures:
- Liver
- Spleen
- Kidneys
- Left Renal Sinus
- Renal Collecting System
- Aorta
- Inferior Vena Cava
- Left Renal Vein
- Superior Mesenteric Artery
- Superior Mesenteric Vein
- Transverse Colon
- Descending Colon
- Linea Alba

Abdominal Compartments
Sometimes pathology helps to demonstrate anatomy. In the top image below, the patient has ascites, which is accumulation of fluid within the peritoneal cavity. The image below that is from a patient without ascites. The presence of ascities highlights the extent of the intraperitoneal versus retroperitoneal compartments. Fluid is darker (lower attenuation) than the surrounding abdominal wall musculature. Note how the intraperitoneal compartment is essentially bathed in ascites fluid (all around the liver, spleen, and intestines). The retroperitoneal space, where the kidneys, aorta, and vena cava reside, is not in contact with the ascites fluid. Notice these structures are surrounded by the retroperitoneal fat.
Identify the following structures:
- Right Kidney
- Liver
- Spleen
- Gas In Intestines
- Ascites Fluid

MRI Imaging
Axial Abdomen
MRI has better soft tissue contrast than CT, and can provide certain details that a CT image cannot. This is an axial T1-weighted MRI of the abdomen. Remember that fat appears bright on a T1-weighted image and soft tissue elements (e.g. organs) appear an intermediate shade of gray. In this particular MRI sequence, moving blood appears black. Identify normal anatomy.
Identify the following structures:
- Right Lobe Of The Liver
- Left Lobe Of The Liver
- Falciform Ligament With Fat Around It
- Spleen
- Kidneys
- Aorta
- Inferior Vena Cava
- Superior Mesenteric Artery
- Pancreas
- Portal Vein
- Retroperitoneal Space (Fat)

Coronal Abdomen
This is a T1-weighted coronal view of the abdomen. Identify normal anatomy.
Identify the following structures:
- Liver
- Spleen
- Diaphragm
- Kidneys
- Psoas Major Muscle
- Descending Colon


