System
Reproductive Imaging

Bony Pelvis
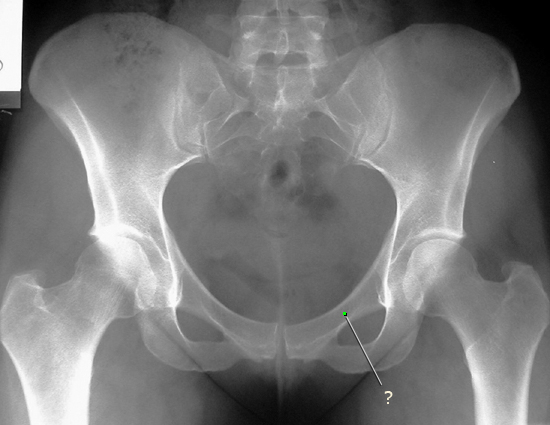
AP Pelvis: Male and Female
Compare the two pelvis radiographs. The first radiograph is from a male, and the second radiograph is from a female. Note the differences in the shape of the pelvis between sexes.
Identify the following structures:
- Iliac Crest
- Sacroiliac Joint
- Obturator Foramen
- Ischial Tuberosity
- Pubic Symphysis
- Pubic Arch
- Ischial Spine

AP Sacrum
This is an AP View of the sacrum. Since the sacrum is tilted posteriorly, this view is obtained with the x-ray beam directed at a slight angle; from inferior to superior in order to obtain a true AP view of the body of the sacrum. Note this view distorts other bony structures of the pelvis. Compare the appearance of the sacrum on this view to the prior AP views of the pelvis.
Identify the following structures:
- Sacral Ala
- Sacroiliac Joint
- Anterior Sacral Foramen
- Posterior Sacral Foramen
- Sacral Vertebrae
- Sacrococcygeal Joint
- Coccyx

Lateral Sacrum
This is a lateral view of the sacrum. The right side of the film is posterior, and the left, anterior.
Identify the following structures:
- Sacral Promontory
- 5th Lumbar Vertebral Body
- 5 Sacral Vertebrae
- Sacrococcygeal Joint
- Coccyx

Bony Pelvis Questions
Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
Which structure forms part of the pelvic outlet?
arcuate line
pectineal line
sacral promontory
sacrospinous ligament
sacrotuberous ligament
Pelvic Organs
MRI: Sagittal Pelvis, female
This is a T2-weighted mid-sagittal MRI of the female pelvis. The important relationships between the uterus, bladder, and rectum are demonstrated well in this image. Fluid, such as urine in the bladder, appears bright on this T2-weighted images.
Identify the following structures:
- Uterus
- Cervix
- Vaginal Canal
- Bladder
- Pubic Bone
- Rectum
- Coccyx

CT: Axial Pelvis, female
This is an axial CT scan of a female pelvis. Intravenous and oral contrast material was administered prior to obtaining the scan.
Identify the following structures:
- Uterus
- Round Ligaments
- Rectum
- Loops Of Small Bowel
- Iliopsoas

CT: Axial Pelvis, male
Identify the following structures:
- Bladder
- Rectum
- Seminal Vesicles
- Obturator Internus
- Right Femoral Head In Acetabulum

Hysterosalpingogram
This is a study of the uterus and uterine (fallopian) tubes. A catheter is passed through the cervix, and sterile contrast material is injected through it into the uterus. This is performed with fluoroscopic guidance, and radiographs are obtained to document the anatomy. Note the extravasation of the contrast into the intraperitoneal space as it reaches the end of the uterine tubes. This represents the location of the ovaries, and highlights the communication between the uterine tubes and the intraperitoneal space.
Identify the following structures:
- Catheter
- Uterus
- Uterine Tubes
- Extravasated Dye (Intraperitoneal)

Pelvic Organs Questions
Radiology Quiz
Quiz
Anatomy Quiz
Quiz
The prostate is associated with:
apex of the bladder
base of the bladder
inferior surface (neck) of the bladder
superior surface of the bladder
Pelvic Angiography
This is an angiogram of the abdominal aorta and pelvic arteries. The contrast is injected through the catheter and exits at the tip, which is located in the abdominal aorta.
Identify the following structures:
- Catheter
- Lumbar Arteries
- Aorta
- Inferior Mesenteric Artery
- Left Common Iliac Artery
- Left External Iliac Artery
- Left Internal Iliac Artery
- Right Internal Iliac Artery
- Left Inferior Gluteal Artery
- Left Superior Gluteal Artery

Internal Iliac Angiogram
This is a slightly oblique view as you may note by the orientation of the obturator foramina. Note the extensive branching of this left internal iliac artery within the pelvis.
Identify the following structures:
- Catheter
- Vertebral Column
- Iliac Crest
- Pubic Symphysis
- Obturator Foramen
- Internal Iliac Artery
- External Iliac Artery

Breast Imaging
Mammogram
This image represents one of the common mammographic views. The breast tissue is compressed in a medial lateral oblique (MLO) orientation in order to obtain a large surface area for imaging. Fibroglandular tissue, the breast ducts and lobules, comprises the bulk of the dense material seen in a mammogram. All normal breast tissue lies superficial to the pectoralis major muscle, and is separated from this muscle by clavipectoral fascia.
Identify the following structures:
- Nipple
- Fibroglandular Tissue
- Pectoralis Major Muscle
- Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue

Ductogram
A ductogram is a procedure performed to visualize the ductal anatomy of a breast lobe, often to evaluate patients with nipple discharge. A very thin, blunt cannula is inserted into the opening of a particular lactiferous duct, and contrast dye is injected followed by mammographic imaging. This example shows the ductal anatomy of a breast lobe, with reflux of dye into the lobular tubuloalveolar system.
Identify the following structures:
- Lactiferous Duct
- Terminal Ducts
- Tubuloalveolar Gland Lobule